-
Android) CodeLab - Layouts in Jetpack ComposeAndroid 2021. 11. 14. 22:02

Modifiers
- Modifiers는 기존 View에서 xml 속성과 유사한 역할을 하는데, 범위별 Modifiers의 유형 안전성은 특정 레이아웃에 사용 가능하고 적용할 수 있는 항목을 검색하고 이해하는데 도움을 준다.
- 함수의 파라미터로 Modifier를 넣어주는 컨벤션을 사용하면 좋다.
- 전체 영역에 clickable 효과를 주고 싶을 때, padding은 clickable 뒤에 적용해주자.
- CompositionLocalProvider : 컴포지션 트리를 통해 암시적으로 데이터를 전달할 수 있다.
@Composable fun PhotographerCard(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { Row( modifier .padding(8.dp) .clip(RoundedCornerShape(4.dp)) .background(MaterialTheme.colors.surface) .clickable(onClick = {}) .padding(16.dp) ) { Surface( modifier.size(50.dp), shape = CircleShape, color = MaterialTheme.colors.onSurface.copy(alpha = 0.2f) ) { } Column( modifier .padding(start = 8.dp) .align(Alignment.CenterVertically) ) { Text("Alfred Sisley", fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold) CompositionLocalProvider(LocalContentAlpha provides ContentAlpha.medium) { Text("3 minutes ago", style = MaterialTheme.typography.body2) } } } }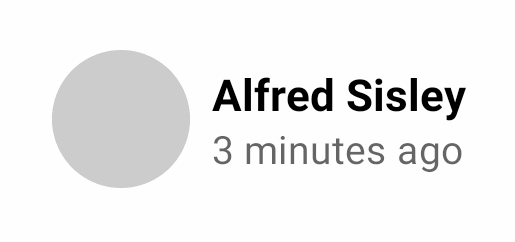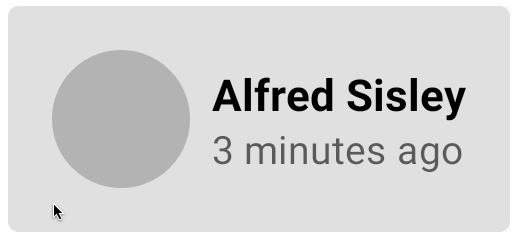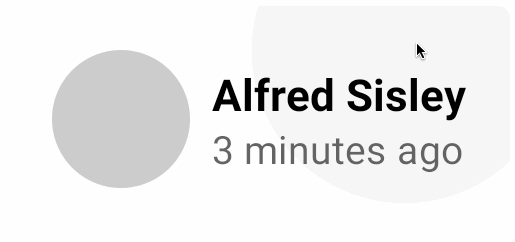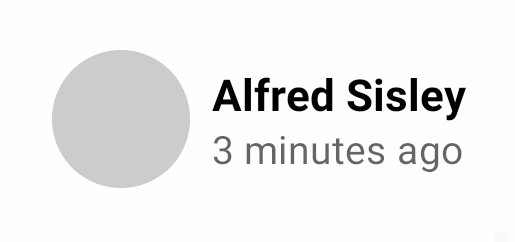
Scaffold
- 가장 높은 수준의 컴포저블.
- Scaffold를 사용하면 기본 Material Design 레이아웃 구조로 UI를 구현할 수 있다.
- TopAppBar, BottomAppBar, FloatingActionButtion 및 Drawer 등을 제공한다.
@Composable fun LayoutsCodelab() { Scaffold( topBar = { TopAppBar( title = { Text(text = "LayoutsCodelab") }, actions = { IconButton(onClick = { /*TODO*/ }) { Icon(Icons.Filled.Favorite, contentDescription = null) } } ) } ) { innerPadding -> BodyContent(Modifier.padding(innerPadding)) } } @Composable fun BodyContent(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { Column(modifier.padding(8.dp)) { Text(text = "Hi there!") Text(text = "Thanks for going through the Layouts codelab") } }
Working with lists
- 컴포즈는 Column과 Row로 리스트를 쉽게 표현할 수 있다.
- Column은 기본적으로 스크롤을 다루지 못한다. verticalScroll 옵션을 통해 스크롤할 수 있다.
- LazyColumn을 통해 보이는 아이템만 리스트에 렌더링 해서 성능을 개선시키자. 기존의 리사이클러뷰와 동일한 개념이다.
- 이미지를 인터넷에서 렌더링 할 때, 스크롤 시에 렌더링이 블라킹 되지 않도록 remeberCoroutineScope를 사용하여 코루틴 스코프 내에서 suspend functions로 사용하자.
@ExperimentalCoilApi @Preview @Composable fun ImageList() { val listSize = 100 val scrollState = rememberLazyListState() val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope() Column { Row { Button(onClick = { coroutineScope.launch { scrollState.animateScrollToItem(0) } }) { Text("Scroll to the top") } Button(onClick = { coroutineScope.launch { scrollState.animateScrollToItem(listSize - 1) } }) { Text("Scroll to the end") } } } LazyColumn(state = scrollState) { items(100) { ImageListItem(it) } } } @ExperimentalCoilApi @Composable fun ImageListItem(index: Int) { Row(verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically) { Image( painter = rememberImagePainter( data = "https://developer.android.com/images/brand/Android_Robot.png" ), contentDescription = "Android Logo", modifier = Modifier.size(50.dp) ) Spacer(Modifier.width(10.dp)) Text("Item #$index", style = MaterialTheme.typography.subtitle1) } }Create your custom layout
- 기본적으로 Column, Row, Box를 사용해서 레이아웃을 만들 수 있지만, 특별한 경우는 Layout 컴포저블을 사용할 수 있다.
- Principles of Layout in Compose - 컴포즈 UI는 다중 측정을 허용하지 않는다. 자식을 두 번 이상 측정할 수 없음을 의미한다. 즉 오직 한 번만 자식을 측정한다.
@Composable fun MyOwnColumn( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, content: @Composable () -> Unit ) { Layout( modifier = modifier, content = content ) { measurables, constraints -> // Don't constrain child views further, measure them with given constraints // List of measured children val placeables = measurables.map { measurable -> // Measure each child measurable.measure(constraints) } // Track the y co-ord we have placed children up to var yPosition = 0 // Set the size of the layout as big as it can layout(constraints.maxWidth, constraints.maxHeight) { // Place children in the parent layout placeables.forEach { placeable -> // Position item on the screen placeable.placeRelative(x = 0, y = yPosition) // Record the y co-ord placed up to yPosition += placeable.height } } } } @Composable fun BodyContent(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { MyOwnColumn(modifier.padding(8.dp)) { Text("MyOwnColumn") Text("places items") Text("vertically.") Text("We've done it by hand!") } }Complex custom layout
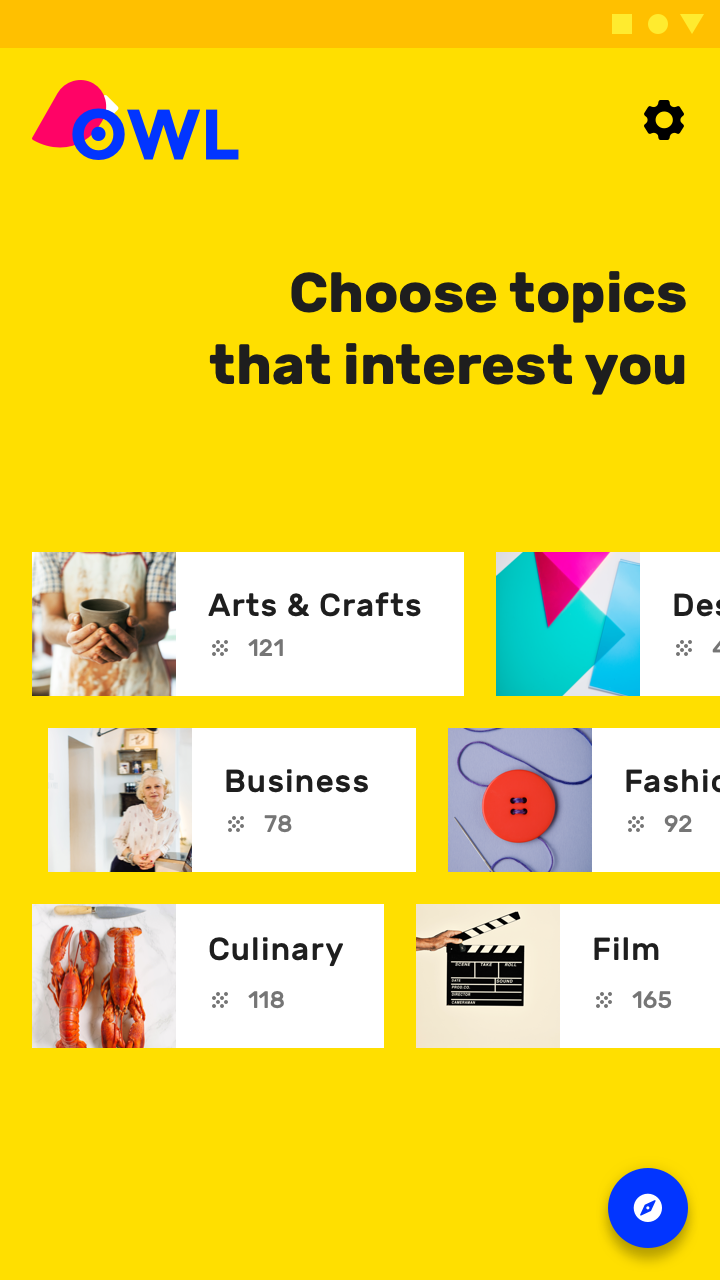
- 다음과 같은 복잡한 레이아웃(staggerd grid layout)을 구성하기 위해 Column과 Row만으로는 불가능하다. 레이아웃의 staggering(지그재그)을 표현할 수 없기 때문이다.
- 그래서 이런 복잡한 레이아웃도 위에서 배웠던 custom layout을 사용하여 표현할 수 있다.
- 자식을 오직 한번만 측정할 수 있음을 기억하자.
더보기@Composable
fun Chip(modifier: Modifier = Modifier, text: String) {
Card(
modifier = modifier,
border = BorderStroke(color = Color.Black, width = Dp.Hairline),
shape = RoundedCornerShape(8.dp)
) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier.padding(start = 8.dp, top = 4.dp, end = 8.dp, bottom = 4.dp),
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(16.dp, 16.dp)
.background(color = MaterialTheme.colors.secondary)
)
Spacer(Modifier.width(4.dp))
Text(text = text)
}
}
}
val topics = listOf(
"Arts & Crafts", "Beauty", "Books", "Business", "Comics", "Culinary",
"Design", "Fashion", "Film", "History", "Maths", "Music", "People", "Philosophy",
"Religion", "Social sciences", "Technology", "TV", "Writing"
)
@Composable
fun BodyContent(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Row(modifier = modifier.horizontalScroll(rememberScrollState())) {
StaggeredGrid {
for (topic in topics) {
Chip(modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp), text = topic)
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun StaggeredGrid(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
rows: Int = 3,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
Layout(
modifier = modifier,
content = content
) { measurables, constraints ->
val rowWidths = IntArray(rows) { 0 }
val rowHeights = IntArray(rows) { 0 }
val placeables = measurables.mapIndexed { index, measurable ->
val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints)
val row = index % rows
rowWidths[row] += placeable.width
rowHeights[row] = Math.max(rowHeights[row], placeable.height)
placeable
}
val width = rowWidths.maxOrNull()
?.coerceIn(constraints.minWidth.rangeTo(constraints.maxWidth)) ?: constraints.minWidth
val height = rowHeights.sumOf { it }
.coerceIn(constraints.minHeight.rangeTo(constraints.maxHeight))
val rowY = IntArray(rows) { 0 }
for (i in 1 until rows) {
rowY[i] = rowY[i - 1] + rowHeights[i - 1]
}
layout(width, height) {
val rowX = IntArray(rows) { 0 }
placeables.forEachIndexed { index, placeable ->
val row = index % rows
placeable.placeRelative(
x = rowX[row],
y = rowY[row]
)
rowX[row] += placeable.width
}
}
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
fun ChipPreview() {
BasicCodelabTheme {
BodyContent()
}
}
Constraint Layout
- 컴포즈에도 Constraint Layout이 있다. 기본 레이아웃보다 더 복잡한 레이아웃을 구현할 때 유용하다.
- createRefs() 또는 createRef() 메서드를 사용하여 Constraint Layout의 연결할 수 있다.
- constraintAs라는 modifier를 사용하여 제약 조건을 지정할 수 있도록 한다.
- linktTo를 사용하여 제약 조건을 지정한다.
- parent는 Contstraint Layout에 대한 제약 조건을 지정하는 데 사용할 수 있는 기존 레퍼런스.
@Composable fun ConstraintLayoutContent() { ConstraintLayout { // Create references for the composables to constrain val (button, text) = createRefs() Button( onClick = { /* Do something */ }, // Assign reference "button" to the Button composable // and constrain it to the top of the ConstraintLayout modifier = Modifier.constrainAs(button) { top.linkTo(parent.top, margin = 16.dp) } ) { Text("Button") } // Assign reference "text" to the Text composable // and constrain it to the bottom of the Button composable Text("Text", Modifier.constrainAs(text) { top.linkTo(button.bottom, margin = 16.dp) // Centers Text horizontally in the ConstraintLayout centerHorizontallyTo(parent) }) } }
Intrinsics
- 계속 강조하는 부분이 컴포즈는 자식을 한 번만 측정해야 한다는 것이다. 두 번 측정할 경우 런타임 에러가 발생한다.
- 그러나, 자식을 측정하기 전에 정보가 필요할 경우가 있다.
- 이때, Intrinsics가 실제로 측정되기 전에 쿼리에 대해 알려주는 역할을 한다.
- intrinsicWidth와 intrinsicHeight를 통해 너비와 높이를 알아낸다.
@Composable fun TwoTexts(modifier: Modifier = Modifier, text1: String, text2: String) { Row(modifier = modifier.height(IntrinsicSize.Min)) { Text( modifier = Modifier .weight(1f) .padding(start = 4.dp) .wrapContentWidth(Alignment.Start), text = text1 ) Divider( color = Color.Black, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxHeight() .width(1.dp) ) Text( modifier = Modifier .weight(1f) .padding(end = 4.dp) .wrapContentWidth(Alignment.End), text = text2 ) } }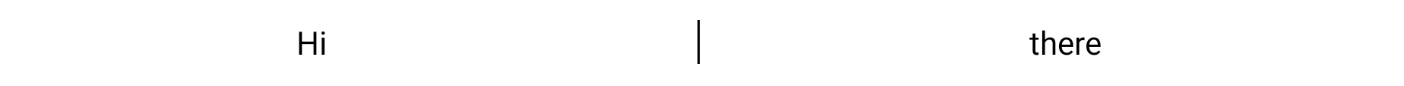 반응형
반응형'Android' 카테고리의 다른 글
Android) Jetpack Compose에서 Paging 라이브러리 사용해보기 (0) 2021.12.04 Android) Jetpack Paging3 유닛 테스트 해보자 (0) 2021.11.28 Android) CodeLab - Jetpack Compose basics (0) 2021.11.02 Android) Jetpack Compose를 시작해보자 (0) 2021.10.02 Android) MVI 아키텍처 살펴보기 (0) 2021.09.26